Performance and stability are two important factors in chemical applications. As a matured Thermal Analysis instrument, the Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) is able to detect changes in heat flow during the heating or cooling process of certain substances, which has become the main indicator for researchers to understand the thermal properties of such materials. Properties like melting point, crystallinity, glass transition temperature, and thermal stability significantly influence material synthesis, processing and end use.
Working principle of differential scanning calorimeter
The energy difference between the sample and reference material is measured during temperature changes, and the working principle of the SKZ1052 Differential Scanning Calorimetery. A sample absorbs or releases heat during a physical or chemical change, for example, a phase transition or reaction, generating a temperature difference with respect to the reference. These slight temperature changes are precisely logged by the DSC system and transformed into heat flow signals, which are examined to study thermal parameter.
 SKZ1052 Differential Scanning Calorimeter
SKZ1052 Differential Scanning Calorimeter
How to test?
A suitable quantity of resin samples needs to be prepared prior to conducting the SKZ1052 DSC test. Wear gloves, ensure uniform samples (up to 50g), dry, free of airborne moisture or contaminants.
Test steps:
1. Load the sample and reference material into the sample and reference cell chambers of the DSC instrument.
2. Set the temperature rate 10 °C/min from room temperature to 200 °C for the test.
3. Run a test; the DSC system automatically logs the heat flow difference between sample and reference.
4. Interpret the DSC curve to get the relevant thermal property data.
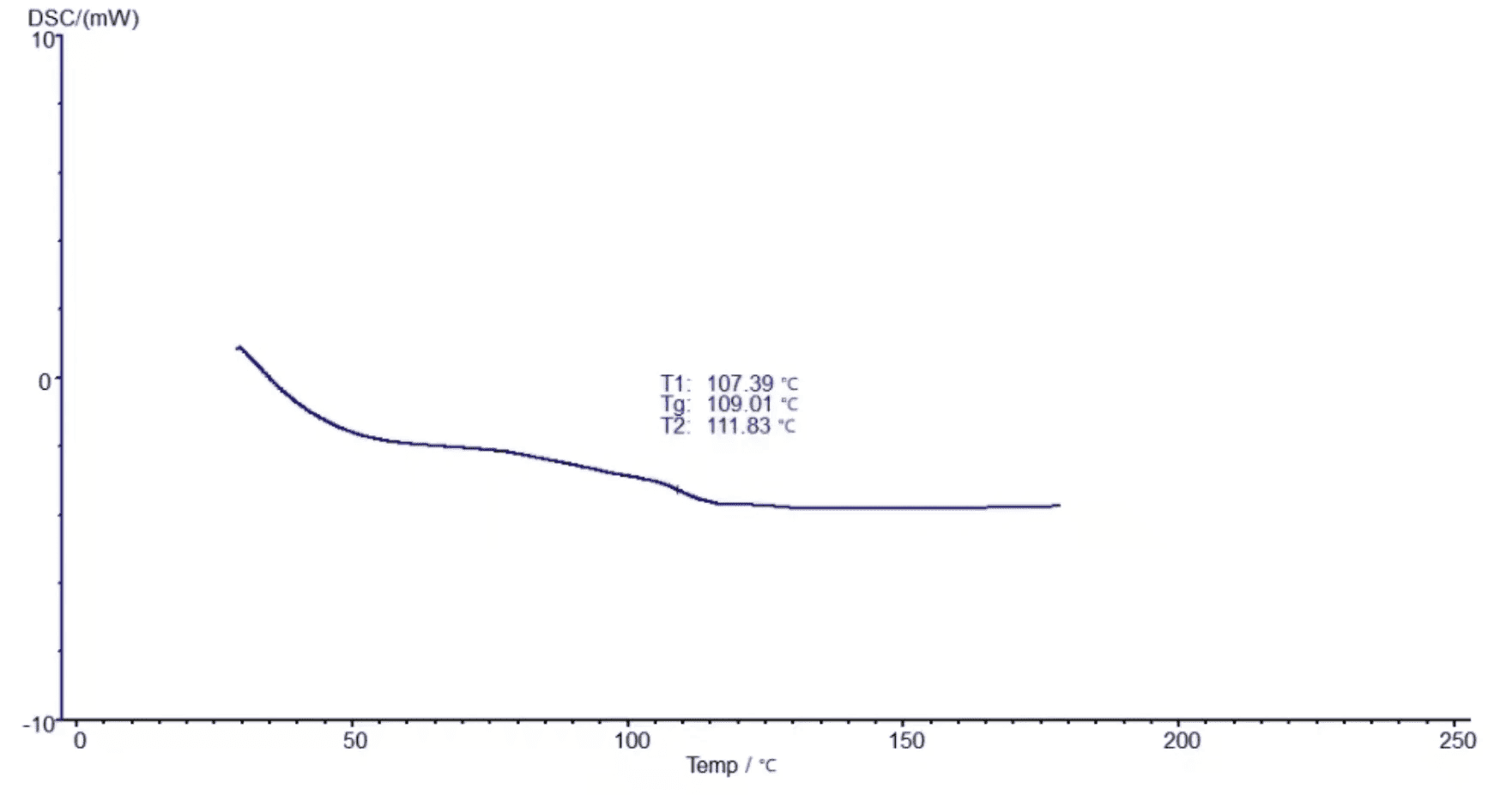 SKZ1052 Test Results
SKZ1052 Test Results
Summary
By means of this chart analysis of temperature, DSC technology improves our understanding in regards to the thermal behavior of chemical products while also allowing the development of materials science.
Interested in this SKZ1052 differential scanning calorimeter? Contact us and let’s explore its infinite possibilities together!